If you’re in the market for a thermal camera for the first time, it can be daunting to select just the right one for your needs. There are numerous options to choose from depending on how you intend to use the camera, for how long, and under what circumstances. Moreover, not all thermal imaging cameras are alike in terms of their features, price, imaging quality, accuracy, and a whole lot of other aspects.
To make the selection process a bit less frustrating for you, this article provides some pointers on how to pick the right thermal camera for your specific needs. In the meantime, let’s get started by looking at what thermal cameras are and how they work.
Thermal Cameras, Their Uses and How They Work
What they are:
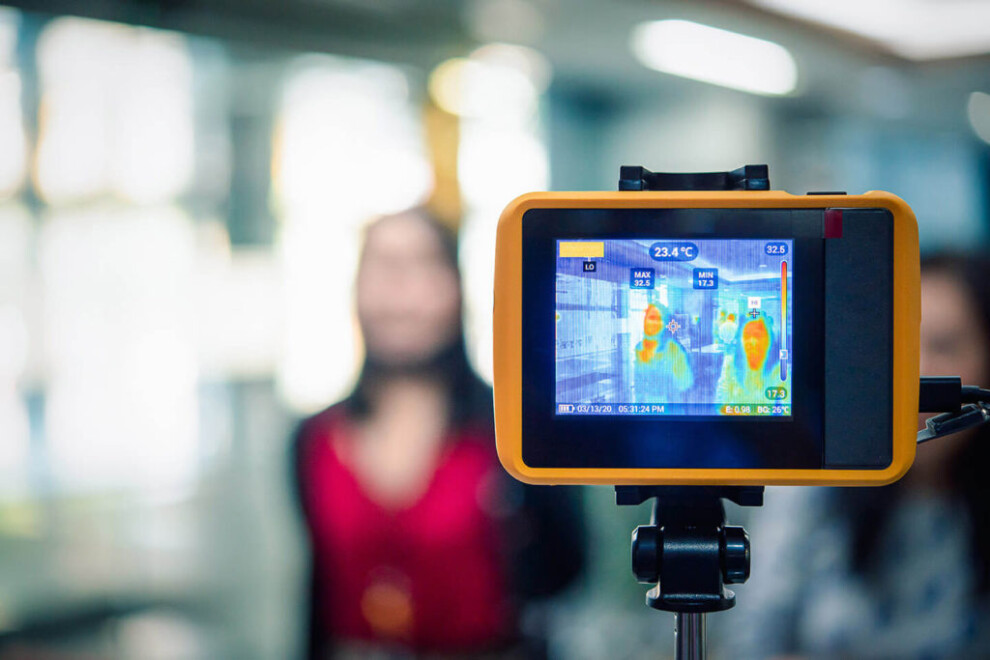
These are simply cameras designed to allow you to see an object using the infrared radiation it emits. Upon focus, what is seen at the camera is an infrared (IR) picture, usually called a thermogram. A version of these cameras called a radiometric thermal camera allows users to determine the temperature at each spot of the thermogram. Nonetheless, this functionality usually depends on various parameters, including object emissivity.
Their uses:
Thermal cameras are utilized in a wide range of applications. For instance, they have been used to look for victims on a chilly night outside, identify smoldering flames inside a wall, or detect hot electrical wires. As early as 1999, thermal imaging cameras were credited with saving multiple lives each year by identifying victims and removing them from poor visibility situations.
As a matter of fact, modern technology makes it possible to attach a thermal camera to your smartphone. There are also several options to pick from when looking for a thermal camera for your Android or iPhone. In a recent review, renowned outdoor enthusiast Randy Angwin compared FLIR One to its pro version and Seek Thermal Compact. This can be a useful guide to check out before approaching your purchase.
Besides the above-mentioned uses, other common applications of thermal cameras include:
- Measuring AC units or heat loss in residences
- Electrical switchboard measurements
- PCB and SMD measurements
Choosing a Thermal Camera: What to Consider
There is barely a one-size-fits-all solution for all applications when it comes to thermal imaging cameras. This means that, including your intended use, you need to consider various factors when choosing your own. Your considerations should include the following.
Camera shape and design:
The conventional thermal camera is held in one hand and fixed to the tripod using a hand strap. The options are numerous, from models the size of a wallet to those with a fixed base and small models that may be used with a smartphone. Some versions provide greater transportation convenience, while others provide a more sturdy solution. Here, it’s all about picking the camera that best suits your job in terms of its design and shape.
Temperature range:
This could be perhaps the most crucial consideration when picking a thermal imaging camera. Basically, it refers to the range of temperatures that the camera is deemed suitable for. So, it is crucial to consider under what temperatures you are likely to be capturing images in the future? Consider temperature disparity if any, because this will affect the image quality as well as the camera’s performance.
Resolution:
The next important thing to think about is camera resolution. Well, most thermal cameras will have pixel counts lower than those of visible-light cameras. This makes it crucial to consider camera resolution, perhaps based on your expected target objects and imaging area. If you expect to be dealing with small objects, make sure to get a high-resolution camera.
Image fusion:
Thermal pictures must be compared to visible light images in specific applications to clearly display temperature differences. Some thermal cameras can easily distinguish between thermal and visual pictures, making image acquisition considerably easier in these situations.
Accuracy and consistency:
Apart from detecting temperature differences, thermal imaging cameras are also used to measure those differences. If you intend to use your camera for the latter purpose, you will want to consider accuracy and consistency. For the best results, go for a thermal camera with an accuracy rating of ±2% if not better.
Sensitivity:
Accuracy goes hand in hand with a parameter referred to as temperature sensitivity, which is often proportional to a specific resolution value assigned by the manufacturer. A higher sensitivity means that the camera can record the smallest temperature differences that can be detected by the camera.
The angle of view:
Just like when selecting another camera, the angle of view is an essential consideration when picking an IR camera. It is related closely to the focal length, whereby the focal length increases as the angle of view decreases. Of course, the values could be changed by introducing more lenses because the distance from the target object and the angle of view are inversely proportional.
Finally, you will need to consider quality, price, and durability. This is especially if you intend to use it for purposes like high-end security surveillance, or monitoring critical infrastructure. If your thermal camera will be sitting outdoors for long periods or moved around often, durability is a crucial consideration.